7 QC Tools: Histogram, Pareto, Fishbone, Scatter Diagram Explained
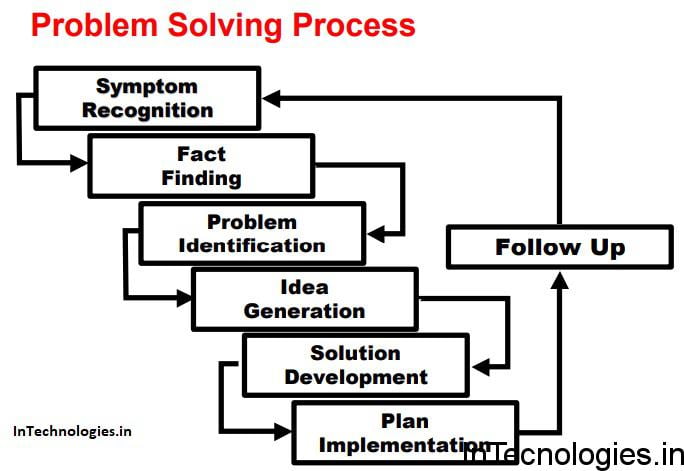
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION
The seven basic quality tools which can be assist and the organization for the problem solving and process the improvements. The first guru who a proposed seven the basic tools was Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa in 1968 by the publishing book entitled Gemba no (QC) Shao the concerned managing quality through the techniques and practices for the Japanese firms. It is the intended to be the applied for self-study training of the employees by foremen or in (QC) reading groups in the Japan. It is in this book that is the seven basic quality the control tools were the first proposed. Valuable resource when applying the seven basic tools Omicron and the Ross 2004. These seven basic quality the control tools which introduced by Dr. Ishikawa are.
“Problem solving, the isolation and analysis of a problem and the development of a permanent solution, is an integral part of the quality-improvement process”. – Not hit or miss, but objective and systematic – Not directed at symptoms, but rather at root causes.

1) Check the sheets
2) Graphs the Trend Analysis
3) Histograms
4) Pareto the charts
5) Cause-and-effect diagrams
6) Scatter the diagrams
7) Control charts
Figure 1 indicates the relationships among the seven tools and the utilizations for an identification and the analysis of improvement of quality the Kerzner 2009.

Check Sheet
The check sheets(CS) are the simple forms with the certain formats that is can be aid the user to record data in a firm the systematically. Data are collected and the tabulated on the check sheet to record the frequency of specific events during and the data collection period. They prepare a consistent effective and the economical approach that can be applied in the auditing of quality assurance for the reviewing and to follow the steps in a particular process. Also the help user to be arrange data for the utilization later the Montgomery 2009 Omicron and the Ross 2004. The main advantages of the check sheets are to be the very easily to apply and the understand and it can be make a clear picture of the situation and condition of the organization. They are efficient and the powerful tools to identify frequently problems but they don’t have effective ability to analyse the quality problem into the workplace. The check sheets are in several, three major types are such as Defect-location check sheets; tally check sheets and the defect-cause check sheets Kerzner, 2009. figure is depicted a tally the check sheet that can be used for collecting data during the production process.
It is a method that enables organized collection of data and grouping of data into categories. The function of a check sheet is to present information in an efficient, graphical format. It function is simplification of data collection process by Task Performer himself.

Histogram
Histogram is the very useful tool to describe a sense of the frequency distribution of the observed values of a variable. It is the type of bar chart that visualizes both attribute and the variable data of a product or the process also assists users to show the distribution of data and the amount of the variation within a process. It displays the different measures of the central tendency mean mode and the average. It should be the designed properly for those working into the operation process can easily utilize and the understand them. Also a histogram can be applied to the investigate and identify the underlying distribution of the variable being explored Omicron and the Ross 2004; Forbes and the Ahmed 2011. Figure illustrates a histogram of the frequency of the defects in manufacturing process.
- Histogram is a visual tool for presenting variable data. It organises data to describe the process performance.
- Additionally histogram shows the amount and pattern of the variation from the process.
- Histogram offers a snapshot in time of the process performance. • A histogram is a graphical summary of variation in a set of data.
- The pictorial nature of the histogram enables us to see patterns that are difficult to see in a table of numbers.

Pareto Analysis
The introduced by an Italian economist named Wilfredo Pareto who worked with income and the other unequal distributions in 19th century, he noticed that 80% of the wealth was owned by only 20% of the population. Later, Pareto principle was developed by Juan in 1950. A Pareto chart is special type of the histogram that is easily be apply to find and the prioritize quality problems conditions or their causes of in the organization Juan and the Godfrey 1998 On the other hand it is the type of bar chart that shows the relative importance of variables prioritized in the descending order from left to right side of the chart. The aim of Pareto chart is to be figure out the different kind of nonconformity from the data figures maintenance data, repair data, parts scrap the rates, or other sources Also Pareto chart can be the generate a mean for investigating concerning quality improvement and the improving efficiency material waste energy conservation safety the issues cost reductions etc. as Figure the demonstrated concerning Pareto chart it can be able to improve the production before and the after changes Montgomery 2009 Kerzner 2009 Omicron and the Ross 2004.
- Vilfredo Pareto (1848-1923) Italian economist – 20% of the population has 80% of the wealth. – 20% of your time determines 80% of your productivity.
- Juran used the term “vital few, trivial many”. He noted that 20% of the quality problems caused 80% of the dollar loss.
- Pareto charts are extremely useful because they can be used to identify those factors that have the greatest cumulative effect on the system, and thus screen out the less significant factors in an analysis.

Fishbone Diagram
The Kaoru Ishikawa is the considered by many researchers to be founder and the first promoter of the Fishbone diagram or Cause and the Effect Diagram for the root cause analysis and concept of the Quality Control (QC) circles. Cause and the effect diagram was the developed by the Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa in 1943. It has also two other names that are Ishikawa diagram and the fishbone because the shape of diagram looks like the skeleton of a fish to the identify quality problems based on their degree of the importance Eyestrain 2017. The cause and the effect diagram is a problem-solving tools that investigates and the analyses systematically all the potential or real causes that result in a single effect. On the other hand it is an efficient tool that equips the organization’s management to explore for the possible causes of a problem Juwan and the Godfrey 1998. This is diagram can provide the problem-solving efforts by the gathering and organizing the possible causes reaching a common understanding of the problem exposing gaps in the existing knowledge ranking the most probable causes and the studying each cause Omicron and the Ross 2004. The generic categories of the cause and the effect diagram are usually six elements causes such as environment materials machine measurement man and the method as indicated in the Figure . Furthermore potential causes can be the indicated by arrows entering the main cause arrow Eyestrain 2017.

Scatter Diagram
The scatter diagram (SD) is a powerful tool to draw the distribution of information in two dimensions which helps to detect and the analyse a pattern relationships between two quality and the compliance variables as an independent variable and the dependent variable and the understanding if there is a relationship between them also what kind of the relationship is Weak or strong and the positive or negative. The shape of the scatter diagram often shows the degree and the direction of relationship between two variables and the correlation may reveal causes of the problem. Scatter diagrams are very useful in the regression modelling Montgomery 2009 Oakland 2003. The scatter diagram can be indicate that there is which one of these following correlation between two variables:
a) Positive the correlation;
b) Negative correlation and the
c) No correlation as demonstrated

Flowchart
Flowchart presents a diagrammatic picture that is indicates a series of a symbols to describe the sequence of the steps exist in an operation or the process. On the other hand a flowchart visualize a picture including the inputs activities decision points and the outputs for using and the understanding an easily concerning the overall objective through process. This is a chart as the problem solving tool can be apply methodically to be detect and the analyse areas are points of the process may have potential problems by documenting and the explaining an operation so it is a very useful to be find and the improve quality into the process Forbes and Ahmed 2011 as a shown in a Figure.

Control Chart
The Control chart or Stewart control chart was introduced and the developed by Walter A. Stewart in the 1920s at the Bell Telephone Laboratories and is likely the most technically sophisticated for the quality management Montgomery 2009. Control charts is a special form of the run chart that it is illustrates the amount and nature of variation in the process over time Also it can draw and the describe what has been happening in the process. Therefore it is very important to be apply the control chart because it can be observe and the monitor process to study process that is in the statistical control No problem with the quality accordant to the samplings or samplings are between UCL and the LCL upper control the limit UCL and the lower control limit LCL. Statistical control is not between UCL and the LCL so it means the process is out of control then control can be applied to the fined causes of quality problem as shown in the Figure 8 that a point is in the control and B point is out of control. In addition, this is chart can be utilized for estimating the parameters and reducing the variability in a process Omicron and the Ross 2004. The main aim of the control chart is to prevent the defects in process. It is very essentially for the different businesses and industries the reason is that unsatisfactory products or services are the more coasted than spending expenses of the prevention by some tools like control charts Juan and the Godfrey 1998. A Control Chart is the presented in the following Figure.
- The bounds of the control chart are marked by upper and lower control limits that are calculated by applying statistical formulas to data from the process.
- Data points that fall outside these bounds represent variations due to special causes, which can typically be found and eliminated.
- On the other hand, improvements in common cause variation require fundamental changes in the process.
- The control chart is the fundamental tool of statistical process control, as it indicates the range of variability that is built into a system (known as common cause variation).
- It helps determine whether or not a process is operating consistently or if a special cause has occurred to change the process mean or variance.

CONCLUSION
This is study identified that is a very essential to be apply all seven (QC) tools for the troubleshooting issues with in production processes in the organizations. Doubtlessly all of the aforementioned quality tools should to be considered and the used by management for identifying and the solving quality problems during producing the products and the services. Thus the production processes can to be affected and the improved by multiple factors of these statistical (QC) tools. Also Marko et al. (2009) designed and the developed an effective layout for the using these (QC) in the organizations based on the performance of them in order to the apply appropriately these quality tools for solving quality problems and the quality improvement as a demonstrated in Figure 9. Accordingly the following Figure interprets how the 7 (QC) should be employed from the first step to end of production processes for identifying the problems of a quality performance and the controlling them.



0 Comments